PostgreSQL offers a wide range of inbuilt string functions that allows us to work efficiently with string manipulation. In Postgres, the CONCAT() is a popularly used string function that combines multiple strings into one. It is executed without any separator, which means all the strings will be merged with each other. If a user desires to add a separator between the concatenated strings, then he can use the CONCAT_WS() function instead of the CONCAT() function.
This blog post is going to explain the use of the COCAT_WS() function along with suitable examples.
How Does the CONCAT_WS() Work in Postgres?
The CONCAT_WS() is nothing more than an extended form of the CONCAT() function which allows the users to put a specific separator between the strings to be concatenated. Users must follow the provided syntax to utilize the CONCAT_WS() function in PostgreSQL:
CONCAT_WS(sep, str_1, str_2,..., str_n);
Replace the “sep” argument with any symbol, character, string, etc. of your choice.
Example1: Concatenating Multiple Strings With a Specific Separator
In the following example, we utilize the “-” symbol as a separator between the given strings:
SELECT CONCAT_WS('-', 'Hello John', 'Welcome to the USA');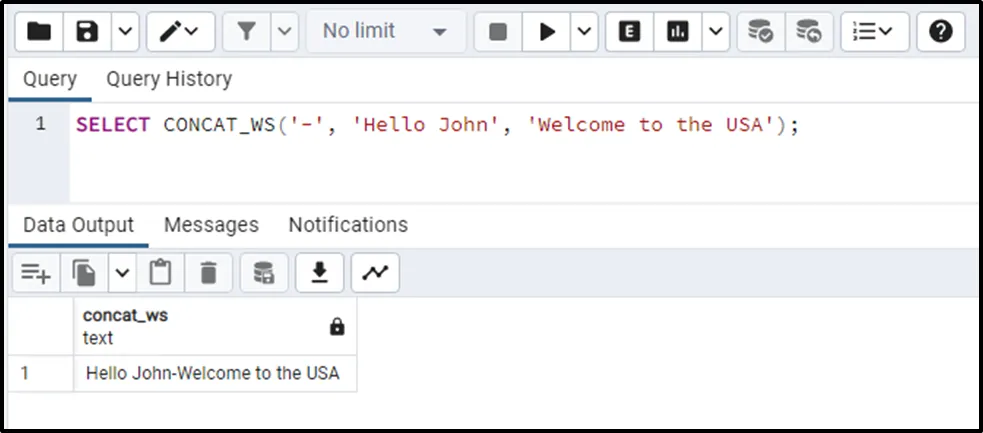
The output signifies that the given strings have been joined/concatenated using the “-” symbol.
Example2: How CONCAT() Differs From CONCAT_WS()?
In this example, we will use the CONCAT() and CONCAT_WS() functions side-by-side to explain the difference between the stated functions:
SELECT CONCAT('Hello John', 'Welcome to the USA'),
CONCAT_WS('-', 'Hello John', 'Welcome to the USA');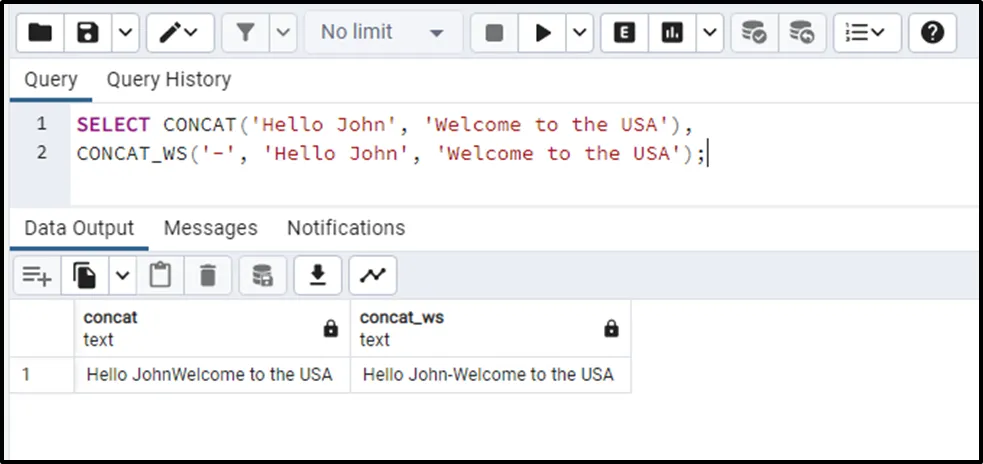
The CONCAT() function combines the given values without any separator while the CONCAT_WS() function combines them according to the specified separator.
Example3: Concatenating Multiple Columns With a Specific Separator
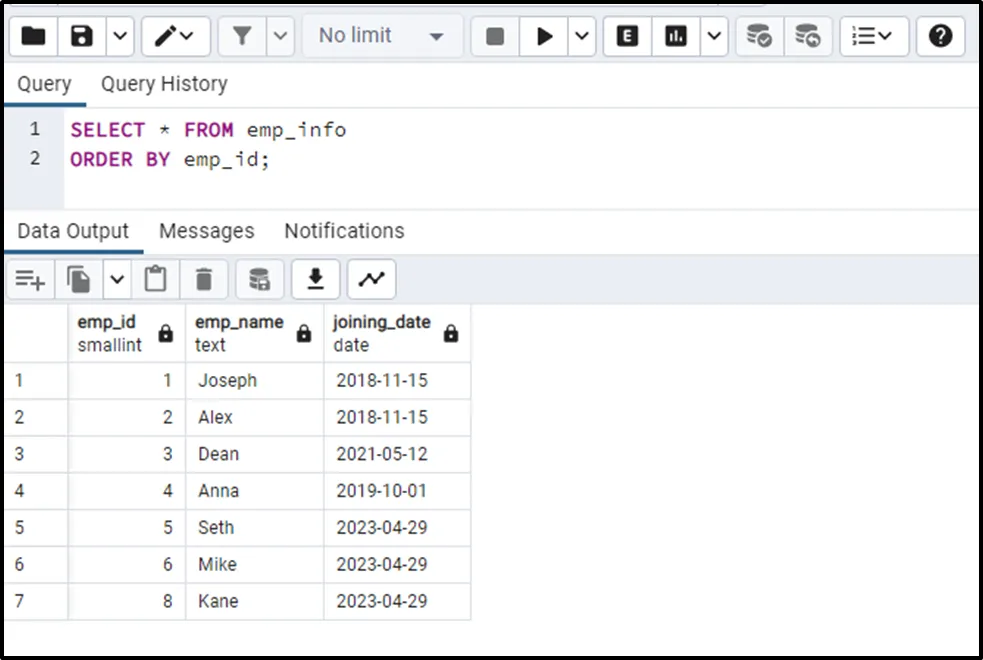
We have created a sample table named “emp_info” with the following data:
SELECT * FROM emp_info ORDER BY emp_id;
Suppose we want to concatenate the table’s column with a specific string. We will utilize a string as a separator:
SELECT CONCAT_WS(' Join on: ', emp_name, joining_date)
FROM emp_info;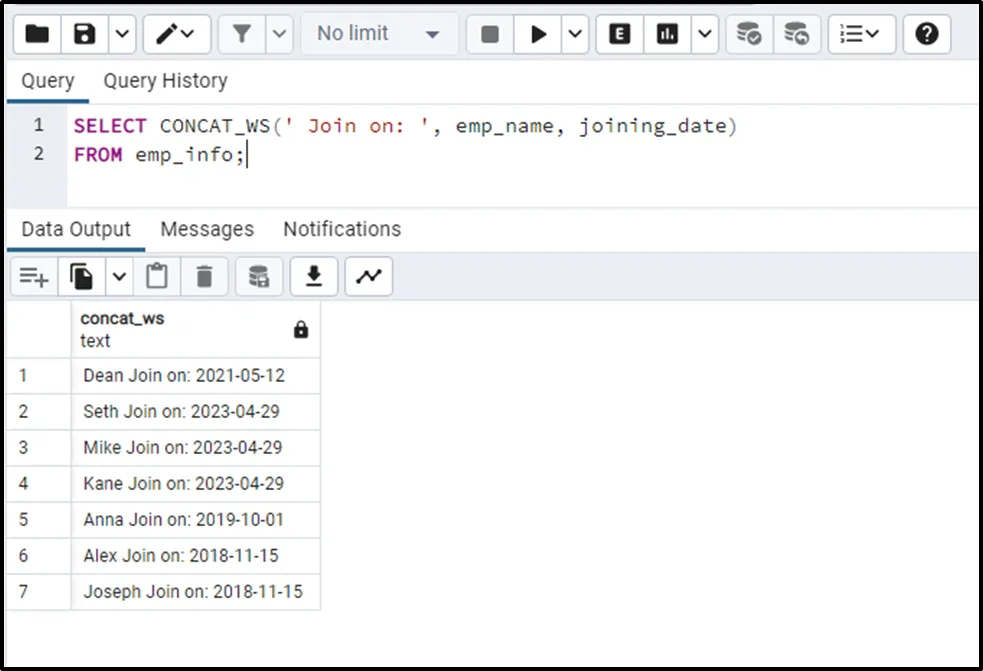
The output depicts that the string “join on:” has been successfully used as a separator between the concatenated columns.
Conclusion
The CONCAT_WS() is an inbuilt string function and an extended form of the CONCAT() function which allows the users to put a specific separator between the strings to be concatenated. The “separator” can be any symbol, character, string, etc. The only difference between the CONCAT() and CONCAT_WS() is that the first one combines the given values without any separator while the other one combines them according to the specified separator. This post has presented an in-depth understanding of the CONCAT_WS() function.



