In PostgreSQL, LIKE, NOT LIKE, and ILIKE operators are used along with the wildcards to perform the pattern matching. Two types of wildcards are used to specify a pattern: a percentage sign “%” and an underscore sign “_”. The percentage wildcard "%" matches sequences of characters, while the underscore "_" matches a single character.
Quick Outline
This write-up will teach you the difference between LIKE, ILIKE, and NOT LIKE operators in PostgreSQL using the following outlines:
- What is a LIKE Operator and How Does it Work in PostgreSQL?
- What is ILIKE Operator and How Does it Work in Postgres?
- What is a NOT LIKE Operator and How Does it Work?
- Wrap Up
So, let’s begin!
What is a LIKE Operator and How Does it Work in PostgreSQL?
The LIKE operator matches the search expression with the specified pattern and retrieves true if the match is found. The LIKE operator is case sensitive, which means it considers “ABC” and “abc” two different strings and hence retrieves false in such a case.
Use the below-specified syntax to perform text matching using the LIKE operator:
SELECT FROM tableName WHERE col_name LIKE pattern;
Use the wildcards to specify a pattern of your choice in place of a pattern.
Read our dedicated guide on Wildcards in PostgreSQL to learn more about wildcards.
Example 1: How Does the LIKE Operator Work?
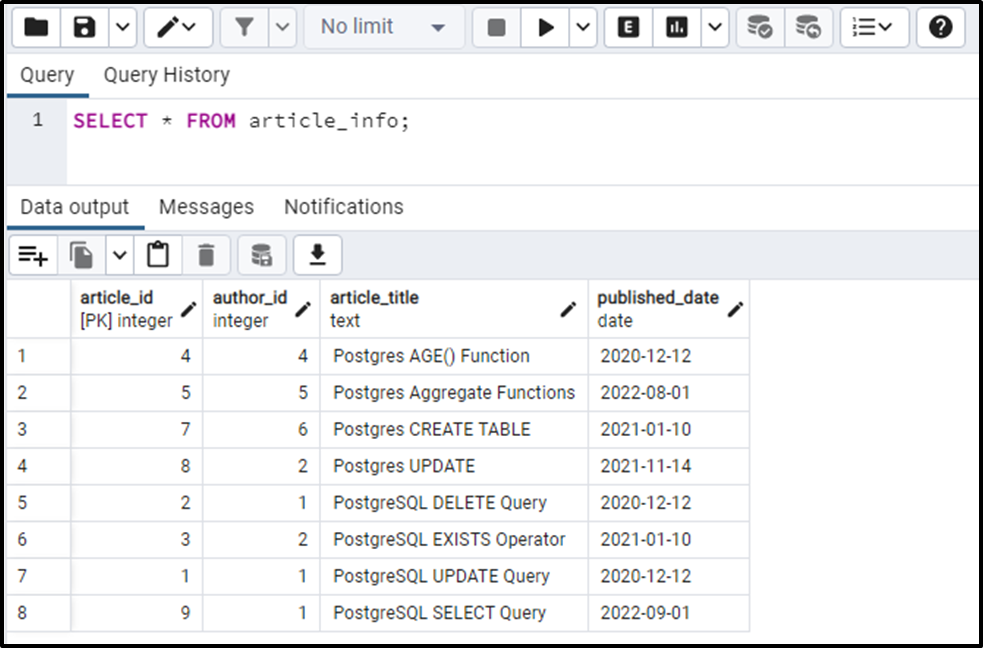
We have created a table named “article_info”, whose data is shown in the following snippet:
SELECT * FROM article_info;
We will utilize the percent wildcard with the LIKE operator to find a substring “Function” from the article_title column:
SELECT article_title FROM article_info WHERE article_title LIKE '%Function%';
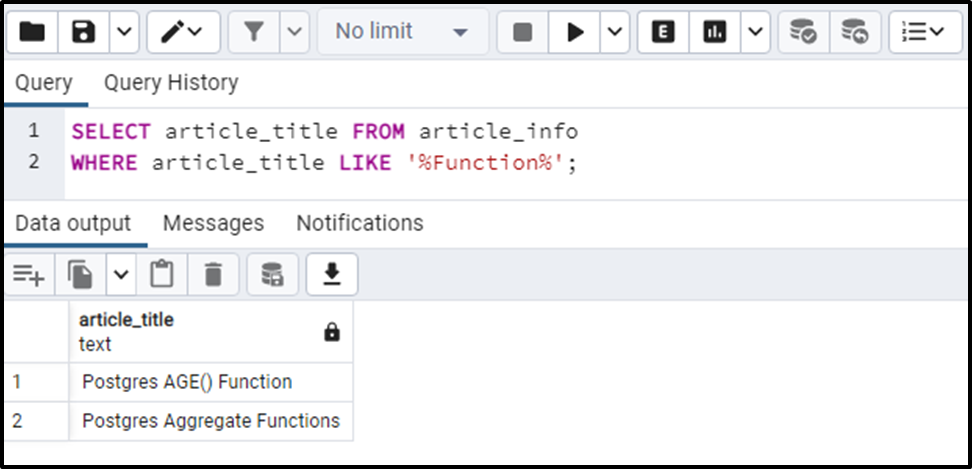
The output snippet proves that two titles in the “artile_info” table contain a substring “Function”.
Example 2: Is the LIKE Operator Case-Sensitive?
The LIKE operator is case-sensitive, so it will retrieve false if the perfect match is not found:
SELECT article_title FROM article_info WHERE article_title LIKE '%function%';
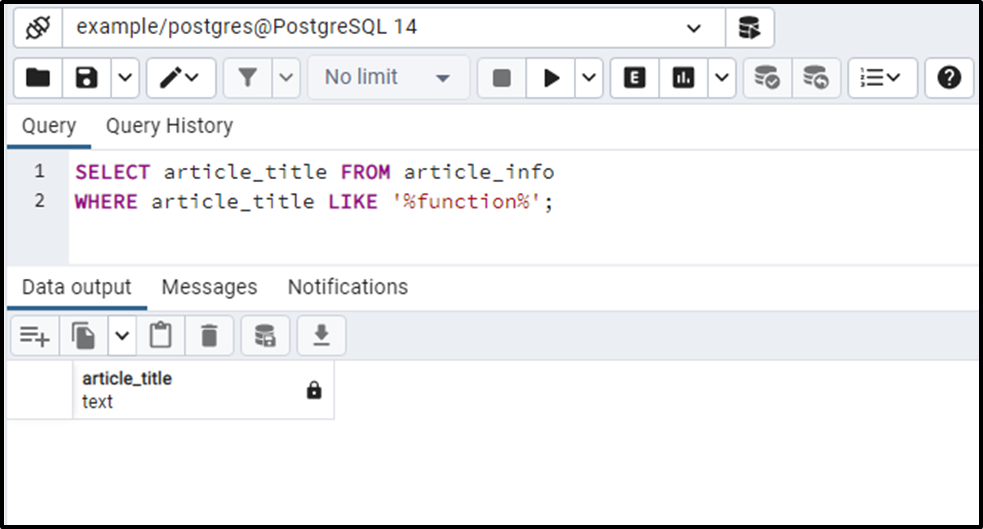
The specified substring "Function" exists in the targeted table; however, the LIKE operator retrieved no record for the specified pattern "%function%". This means the LIKE operator is case-sensitive.
What is ILIKE Operator and How Does it Work in Postgres?
The ILIKE operator matches the search expression with the given pattern irrespective of the letter case. Use the below-specified syntax to perform text matching using the ILIKE operator:
SELECT FROM tab_name WHERE col_name ILIKE pattern;
Example: How Does the ILIKE Operator Work?
Let’s implement the ILIKE operator on the same previous example and see how it works:
SELECT article_title FROM article_info WHERE article_title ILIKE '%function%';
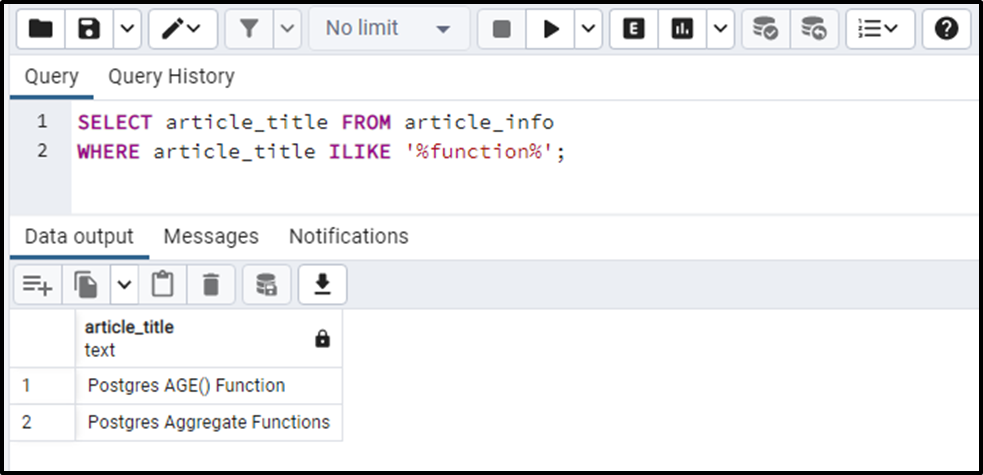
The output snippet proves that the “ILIKE” operator retrieves the data irrespective of the letter case.
What is a NOT LIKE Operator and How Does it Work?
The NOT LIKE operator negates the results of the LIKE operator, which means the NOT LIKE operator will retrieve false if the match is found and true if the match is not found in the string.
Use the below-specified syntax to perform text matching using the NOT LIKE operator:
SELECT FROM tableName WHERE columnName NOT LIKE pattern;
Use the wildcards to specify a pattern of your choice in place of a pattern.
Example: How Does the NOT LIKE Operator Work?
In this example, we will use the NOT LIKE operator instead of the LIKE operator to find all those strings that don’t have the “Function” substring in the article_title column:
SELECT article_title FROM article_info WHERE article_title NOT LIKE '%Function%'
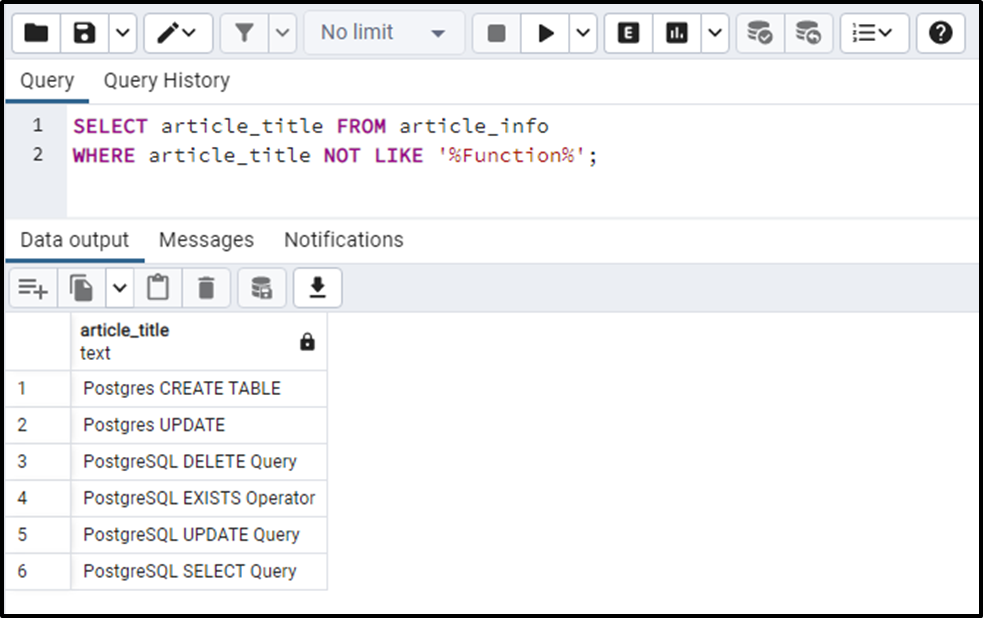
The output shows that the NOT LIKE operator retrieves all the strings other than those that contain a substring “Function”.
Wrap Up
The LIKE operator matches the search expression with the specified pattern and retrieves true if the match is found. The NOT LIKE operator negates the results of the LIKE operator, which means the NOT LIKE operator will retrieve false if the match is found and true if the match is not found in the string. The LIKE operator is case-sensitive while the ILIKE operator matches the search expression with the given pattern irrespective of the letter case. This write-up explains how to use the LIKE, NOT LIKE, and ILIKE operators in Postgres to perform pattern matching.



