PostgreSQL supports various built-in range data types that indicate a span between two different values. It lets us store and manipulate a set of values for different data types like integers, floating point numbers, dates, etc. Moreover, Postgres offers various built-in functions to work with the range types efficiently. This write-up will illustrate one such function named “UNNEST()” that expands a multi-range into a set of range values.
How to Expand a Multi Range Into a Set of Range Values in PostgreSQL?
Use the UNNEST() function along with the “::int4multirange” type to expand multi-range integers into a set of range values in Postgres. Similarly, other range types like “tstzmultirange”, “datemultirange”, etc., can also be used with the UNNEST() function to expand the multi-range values into a set of values (of that particular range type).
Syntax
Use the below-stated syntax to execute the UNNEST() function on the specified multi-range:
UNNEST(multirange ::int4multirange)
Parameters
It accepts a valid multi-range as an argument.
Return Value
The UNNEST() function returns an expanded set of range values which are sorted in ascending order.
Let’s implement the UNNEST() function practically for a profound understanding.
Example 1: Using UNNEST() Function on Multi-range
The following example utilizes the UNNEST() function to expand the specified multi-range into a set of values:
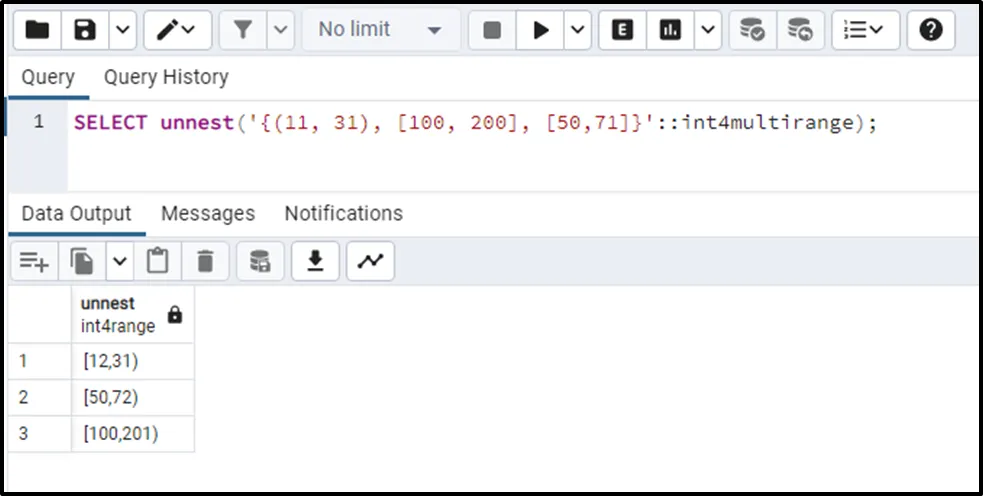
SELECT UNNEST('{(11, 31), [100, 200], [50,71]}'::int4multirange);The output snippet demonstrates that the UNNEST() function retrieves the expanded set of values in ascending order:
Example 2: Using UNNEST() Function on Multi-range Dates
In the following example, the UNNEST() function is executed with the “datemultirange” type to expand the specified multi-range dates into a set of values:
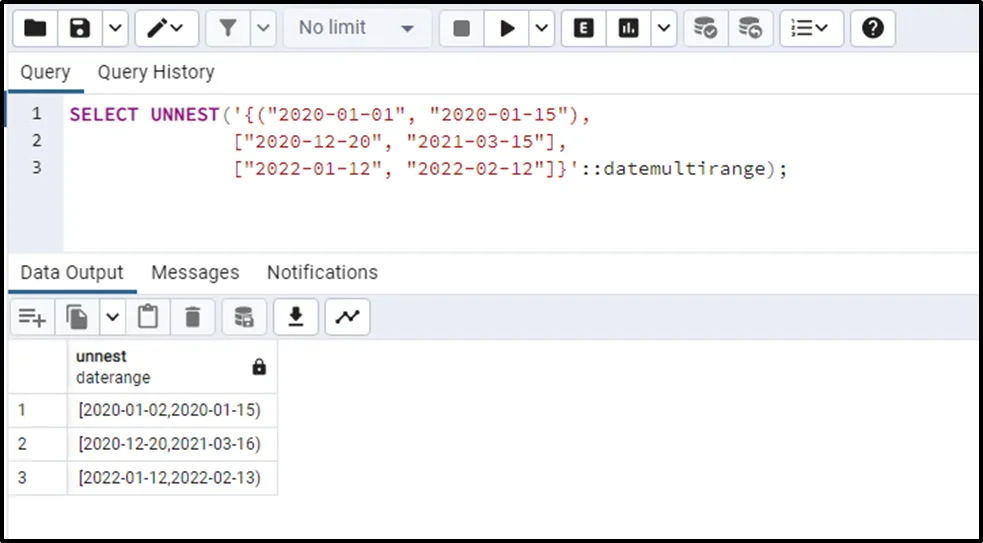
SELECT UNNEST('{("2020-01-01", "2020-01-15"),
["2020-12-20", "2021-03-15"],
["2022-01-12", "2022-02-12"]}'::datemultirange);The stated function retrieves a set of sorted values as follows:
This is how the UNNEST() function works on range types/values in PostgreSQL.
Conclusion
In PostgreSQL, the UNNEST() function is used along with a valid multirange type such as “int4multirange”, “tstzmultirange”, “datemultirange”, etc., to expand multi-range values into a set of range values in Postgres. The UNNEST() function returns an expanded set of range values which are sorted in ascending order. This post has demonstrated a couple of use cases of the UNNEST() function in PostgreSQL using suitable examples.



