PostgreSQL provides numerous Session Functions to control, monitor, and manage individual database sessions. Session functions help us monitor session details, manage session variables, and modify session behavior dynamically. While working with a Postgres database, a common task is retrieving the session start time, which can be done by executing the built-in "pg_postmaster_start_time()" function.
This post demonstrates how to get PostgreSQL server start time using suitable examples.
How to Get PostgreSQL Server Start Time
PostgreSQL offers a built-in “pg_postmaster_start_time()” function that provides the exact timestamp when the server was initiated.
Syntax
The pg_postmaster_start_time() has a very straightforward syntax that includes a SELECT keyword followed by the function name, as shown below:
SELECT pg_postmaster_start_time();
Parameters
The “pg_postmaster_start_time()” function doesn’t accept any argument and must be executed with a set of parentheses.
Return Value
It retrieves a timestamp along with associated zone information which indicates the time when the server was initiated/started.
Return Type
The stated function has a return type “TIMESTAMPTZ” or “TIMESTAMP With Time Zone”.
Example 1: Retrieving Postgres Server Start Time
Let’s execute the pg_postmaster_start_time
SELECT pg_postmaster_start_time() AS server_start_time;
The stated function retrieves the server start time in the following format: “YYYY-MM-DD HH-MM-SS.MS-TZ”:
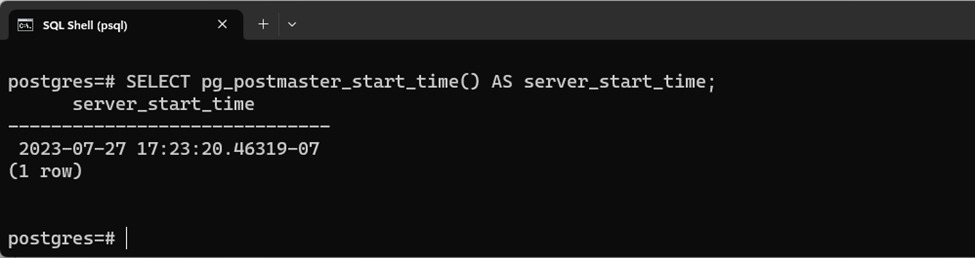
Here, “2023” represents a year, “07” shows a month, “27” indicates a day, “17” represent hours, “23” denote minutes, “20” indicate “seconds”, “46319” represent milliseconds, and “07” describe the server’s time zone.
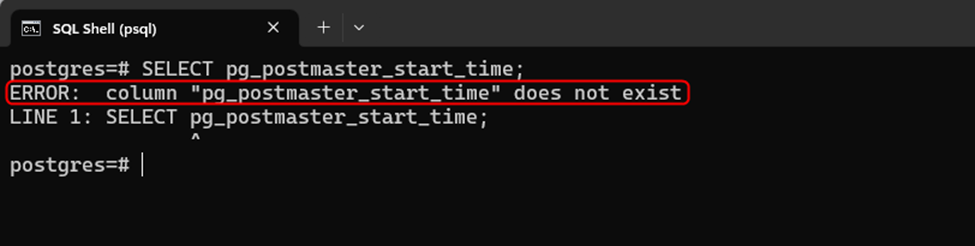
Example 2: ERROR: column "pg_postmaster_start_time" does not exist
The stated function must be executed with a set of parentheses, otherwise a “column "pg_postmaster_start_time" does not exist” error will occur:
SELECT pg_postmaster_start_time;
That’s all about getting the Postgres Server start time using the pg_postmaster_start_time() function.
Conclusion
PostgreSQL offers a built-in “pg_postmaster_start_time()” function that provides the exact timestamp when the server was initiated. The “pg_postmaster_start_time()” function doesn’t accept any argument and must be executed with a set of parentheses. It retrieves a timestamp along with associated zone information which indicates the time when the server was initiated/started. This write-up has illustrated a detailed guide on retrieving the Postgres Server start time using the pg_postmaster_start_time() function.



