Database users often encounter a situation where they need to fetch a specific field from an interval. This may be because of various reasons, such as calculating employees’ experience in years, months, etc., sorting table data based on a specific field, and so on. Postgres offers various inbuilt functions that can help us in such scenarios, such as DATE_PART() and EXTRACT().
This blog will present a profound understanding of getting days, months, and years from an interval in Postgres.
How to Get/Extract Years, Months, and Days From an INTERVAL in Postgres?
The DATE_PART() and EXTRACT() functions are used to get a specific date field such as a year, month, etc. from any date, timestamp, or interval. Utilize the below syntax for the DATE_PART() function to get the days, months, or years from a given interval:
DATE_PART('date_field', interval);Specify the field to be extracted in place of “date_field”.
Alternatively, you can also use the EXTRACT() function with the following syntax to accomplish the same task:
EXTRACT('date_field' FROM interval);Let’s learn this concept using the following examples.
Example 1: Getting Years, Months, and Days From an INTERVAL Using DATE_PART() Function
In the following snippet, we will utilize the DATE_PART() function on an interval to get days, months, and years fields from the given interval:
SELECT DATE_PART('DAY', INTERVAL '10 year 6 month 15 day') AS days,
DATE_PART('MONTH', INTERVAL '10 year 6 month 15 day') AS months,
DATE_PART('YEAR', INTERVAL '10 year 6 month 15 day') AS years;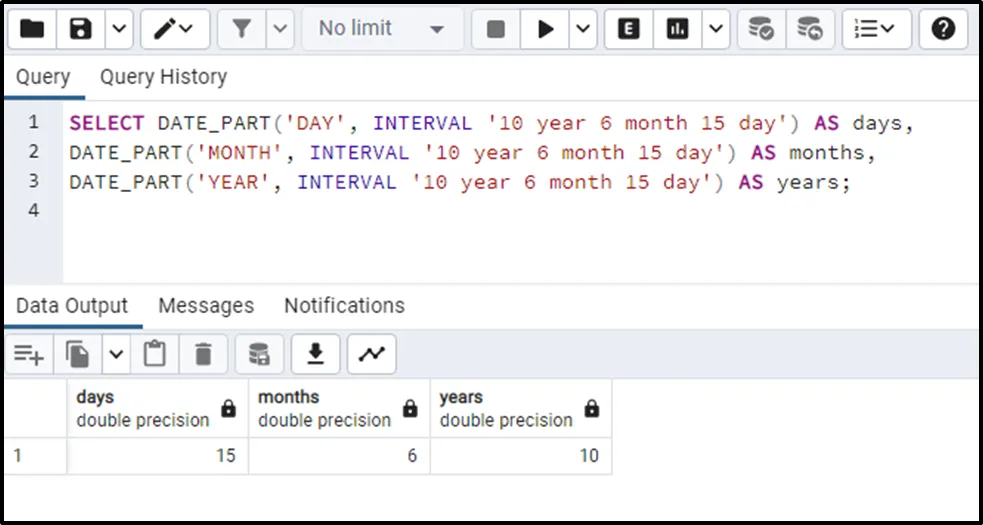
From the output, it can be clearly noticed that the desired date fields have been fetched from the given interval.
Example 2: Getting Years, Months, and Days From an INTERVAL Using EXTRACT() Function
Alternatively, the EXTRACT() function can be utilized with the selected date fields to get the desired results:
SELECT EXTRACT('DAY' FROM INTERVAL '1 year 2 month 15 days') AS days,
EXTRACT('MONTH' FROM INTERVAL '10 year 4 month 15 day') AS months,
EXTRACT('YEAR' FROM INTERVAL '10 year 6 months 15 day') AS years;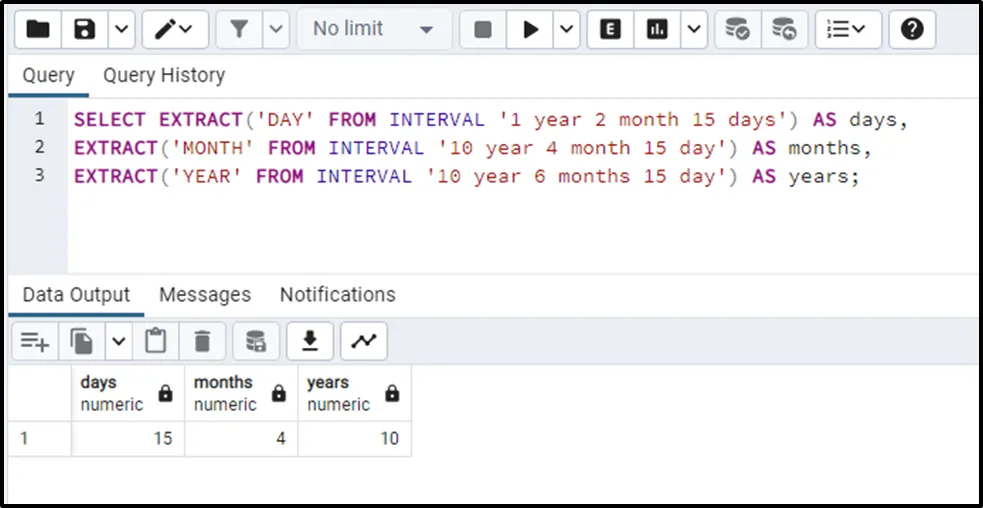
The output shows that the use of the EXTRACT() function retrieves the desired results.
Example 3: Getting Date Fields From the Table’s Data
We have an “article_record” table that contains the following data:
SELECT * FROM article_record;
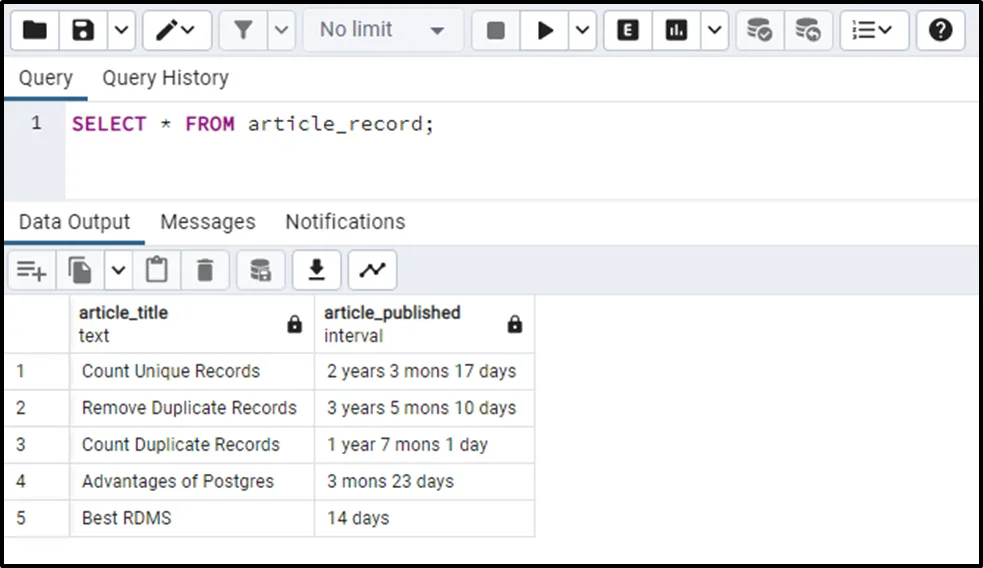
Suppose we want to find the articles’ age in years, months, and days from the given interval. To do that, we can utilize the EXTRACT() or DATE_PART() function as follows:
SELECT article_title, article_published,
EXTRACT('YEAR' FROM article_published) AS year,
EXTRACT('MONTH' FROM article_published) AS month,
EXTRACT('DAY' FROM article_published) AS day
FROM article_record;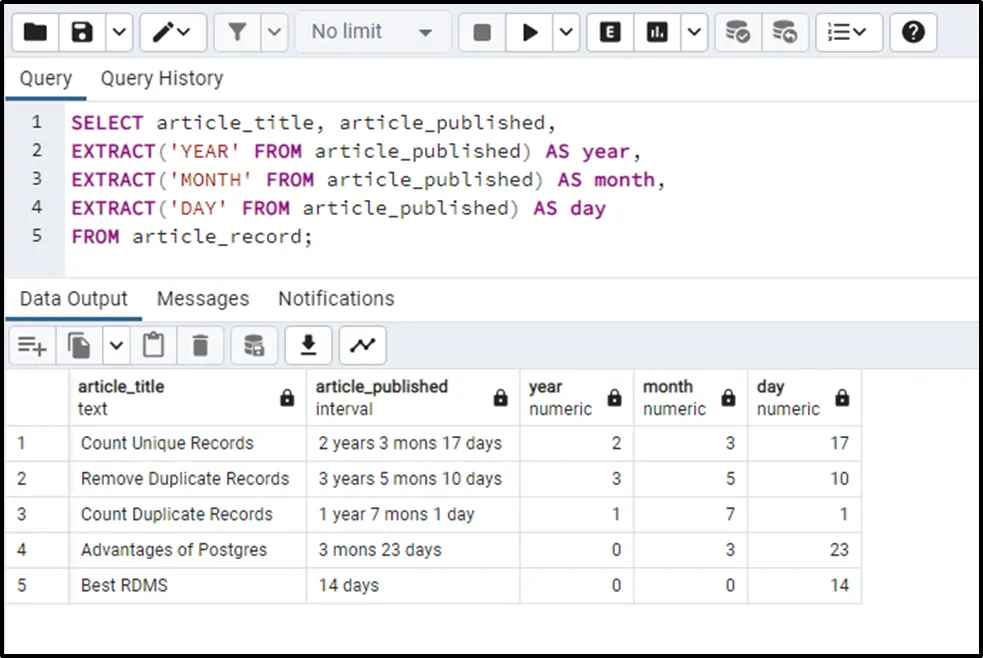
Similarly, users can utilize the DATE_PART() function instead of the EXTRACT() function to get the same functionality.
Conclusion
In PostgreSQL, the DATE_PART() and EXTRACT() functions are used to get a specific date field such as a year, month, etc. from any date, timestamp, or interval. Pass the desired date field and the interval as arguments to the EXTRACT() or DATE_PART() functions to get year, month, and day from the given interval. This post has provided a thorough guide on getting days, months, and years from a specific interval.


