PostgreSQL facilitates us with numerous date and time functions, such as CURRENT_DATE, NOW(), EXTRACT(), etc. These functions allow us to work with the date and time efficiently. In PostgreSQL, different built-in functions are used along with the SELECT statement to query date and time values.
This write-up presents a detailed guide on how to query date and time in Postgres. The below-provided topics will be studied in this blog with appropriate examples:
- How to Query Current DateTime in Postgres?
- How to Find Age/Interval Between Two Timestamps in Postgres?
- How to Query Data Between Two Timestamps Using the BETWEEN Operator?
- How to Get/Extract the Day of the Week From a Specific Timestamp?
- How to Get/Extract a Specific Field From the Given Timestamp?
- How to Convert a Specific Timestamp to a UNIX Timestamp?
How to Query Current DateTime in Postgres?
PostgreSQL facilitates us with numerous date and time functions, such as CURRENT_DATE, NOW(), EXTRACT(), etc. These functions allow us to work with the date and time efficiently. To query the current date or time, the CURRENT_DATE, CURRENT_TIME, NOW(), TIMEOFDAY(), CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, and LOCALTIMESTAMP functions are used in Postgres.
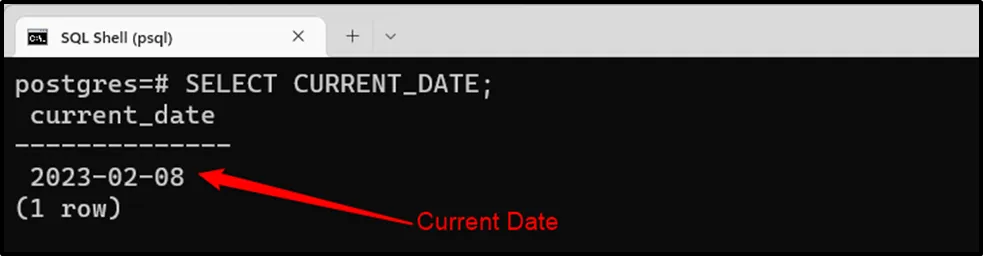
Example 1: CURRENT_DATE Function
Use the CURRENT_DATE function to query the current date only:
SELECT CURRENT_DATE;
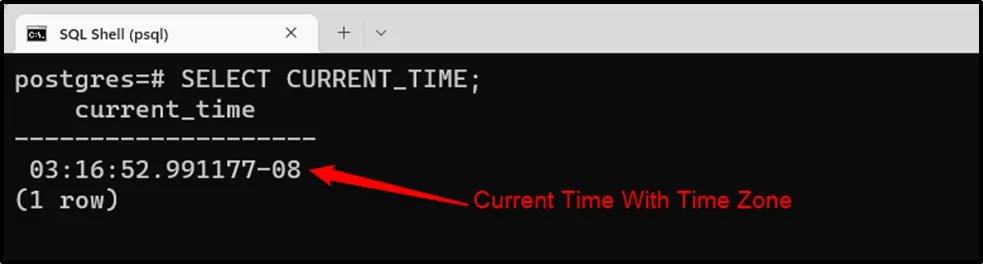
Example 2: CURRENT_TIME Function
Use the CURRENT_TIME function to query the current time only:
SELECT CURRENT_TIME;
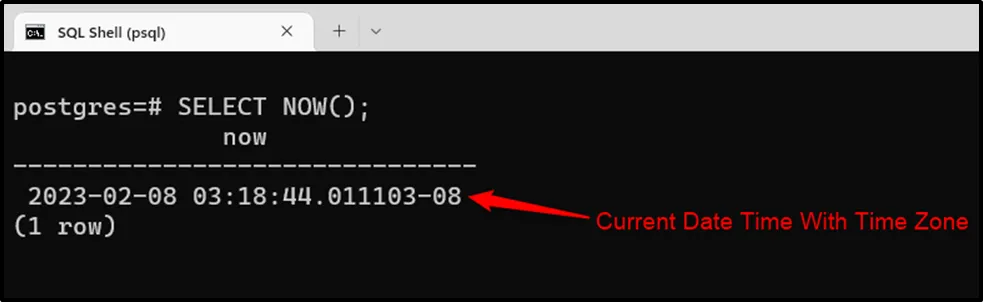
Example 3: NOW() Function
Use the NOW() function to query the current date, time, and timezone:
SELECT NOW();
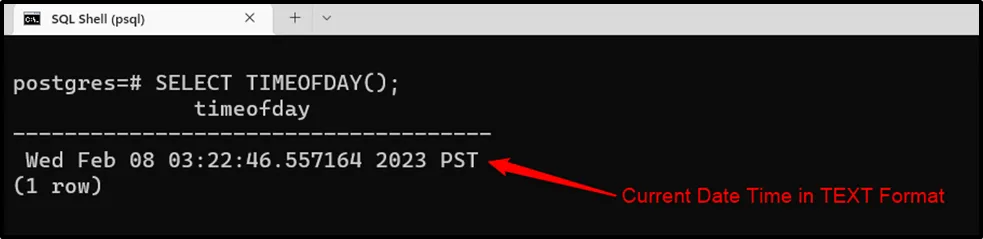
Example 4: TIMEOFDAY() Function
Use the TIMEOFDAY() function to query the current date, time, and time zone in text format:
SELECT TIMEOFDAY();
Example 5: CURRENT_TIMESTAMP Function
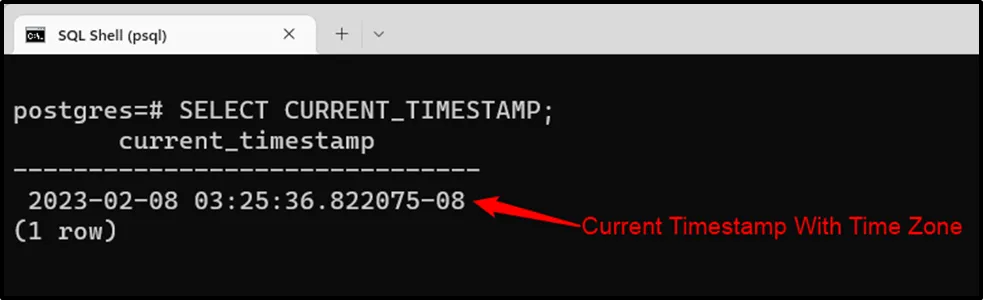
Use the CURRENT_TIMESTAMP to query the current timestamp with the time zone.
SELECT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP;
Example 6: LOCALTIMESTAMP Function
Use the LOCALTIMESTAMP to query the current timestamp without the time zone.
SELECT LOCALTIMESTAMP;

This way, you can use these built-in date time functions to query the current date, current time, or both current date and time in PostgreSQL.
How to Find Age/Interval Between Two Timestamps in Postgres?
In Postgres, AGE() is a built-in function that is used to calculate the ages/intervals. In the following example, we will use the AGE() function to calculate the employee’s total experience in the company. Firstly, let’s describe the table’s data:
SELECT * FROM emp_data;

Let’s learn how to query data between two timestamps using the AGE() function:
SELECT emp_name, emp_joining_date, AGE(CURRENT_DATE, emp_joining_date) AS Experience FROM emp_data ORDER BY emp_id ASC;
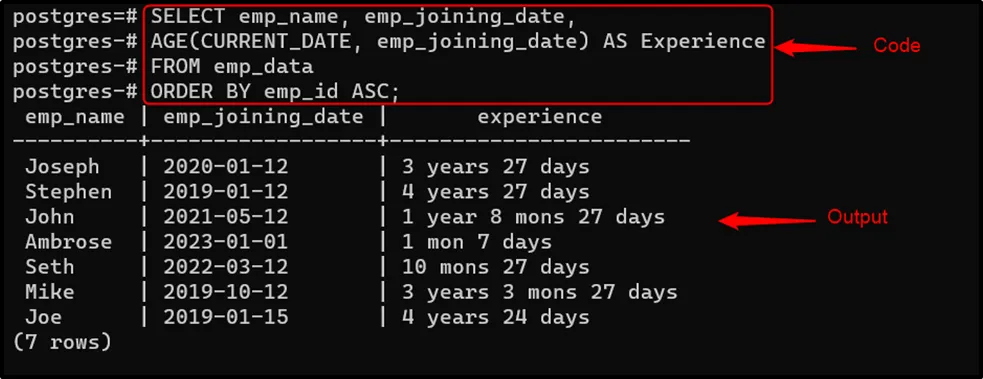
The output shows that the AGE() function retrieves an interval that shows the difference between the current date and the date specified in the “emp_joining_date” column.
How to Query Data Between Two Timestamps Using the BETWEEN Operator?
Suppose we want to find those employees who joined a company between “2020-01-01” and “2023-01-01”. For this purpose, use the BETWEEN operator as follows:
SELECT emp_name, emp_joining_date FROM emp_data WHERE emp_joining_date BETWEEN '2020-01-01' AND '2023-01-01';
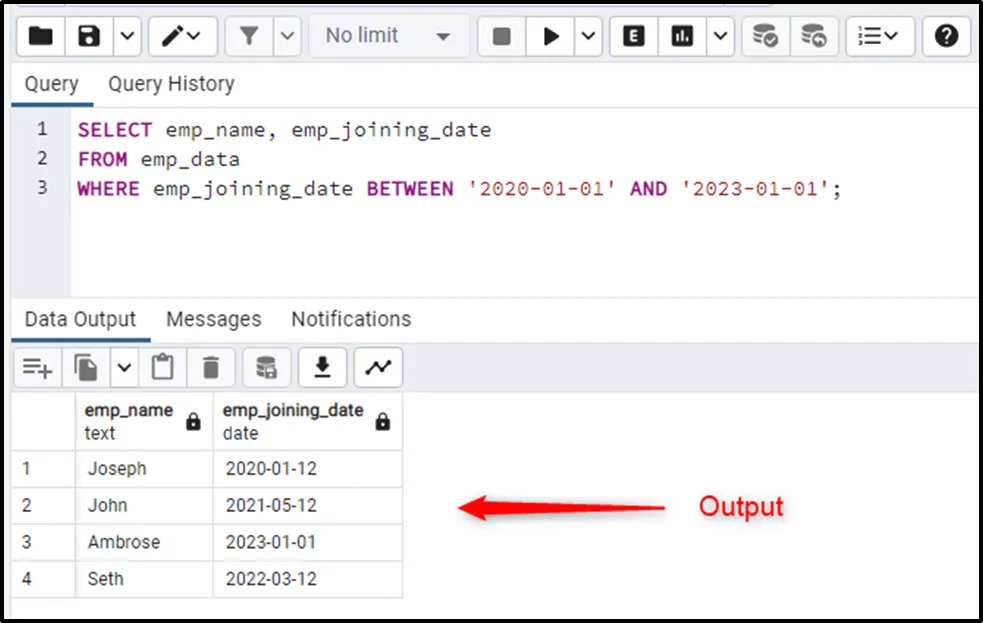
The BETWEEN operator queries the employees’ data between the specified dates only.
How to Get/Extract the Day of the Week From a Specific Timestamp?
In Postgres, the TO_CHAR() function is used with the “DAY” argument to get the day of the week as a String. While the DATE_PART() function is used with the “DOW” argument to fetch the day of the week as an integer/numeric value.
For instance, in the following example, we pass CURRENT_DATE and DAY as arguments to the TO_CHAR() function. As a result, the TO_CHAR() will retrieve the current day of the week:
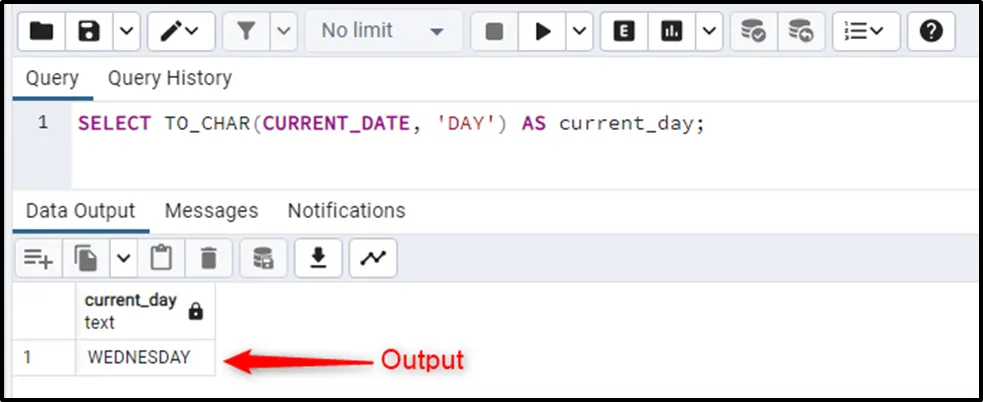
SELECT TO_CHAR(CURRENT_DATE, 'DAY') AS current_day;
Now, pass the CURRENT_DATE function and the ‘DOW’ as arguments to the DATE_PART() function to fetch the week’s current day as an integer/number:
SELECT DATE_PART(CURRENT_DATE, 'DOW') AS current_day;
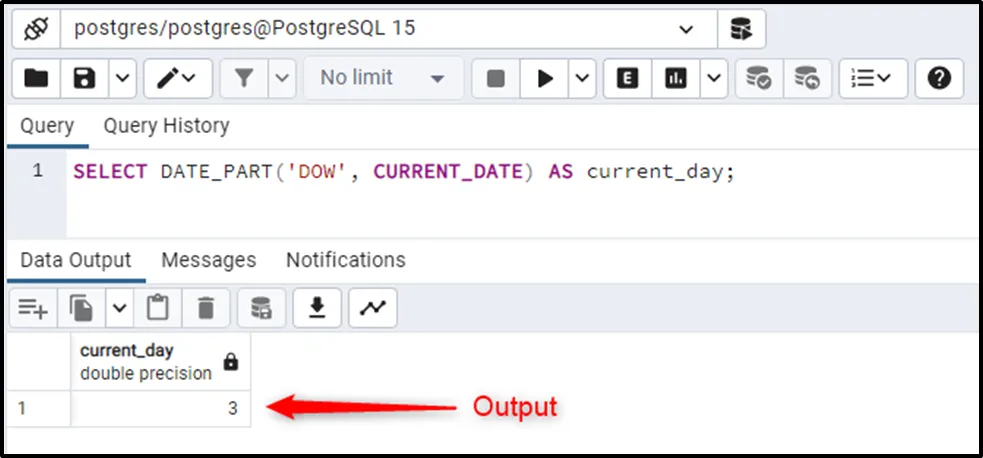
The output states that it's the third day of the week.
How to Get/Extract a Specific Field From the Given Timestamp?
Using the DATE_PART() function, you can extract any part from a timestamp, such as a day, month, year, hour, minute, etc. For this purpose, you must pass a valid format as an argument to the DATE_PART() function.
For instance, in the following code snippet, the DATE_PART() function is used to extract the year from the current timestamp:
SELECT DATE_PART('YEAR', CURRENT_TIMESTAMP) AS current_year;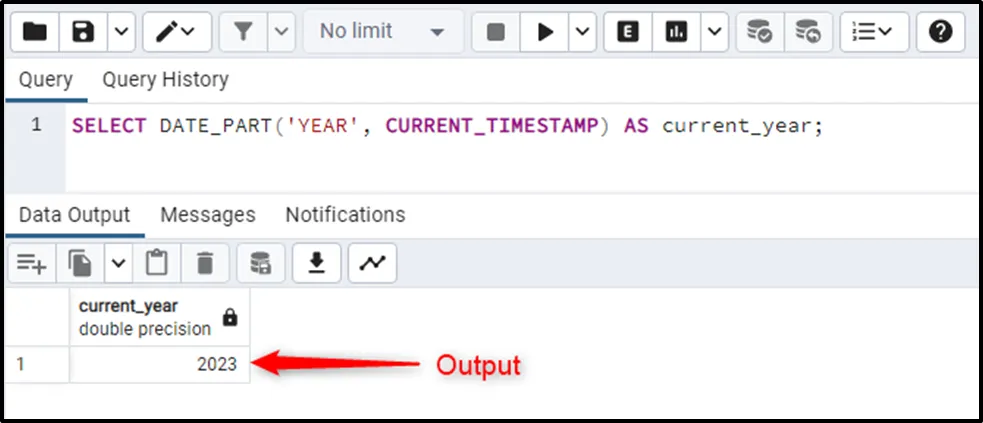
Similarly, you can extract the month, day, day of the week, hours, minutes, etc. from a DateTime field using the DATE_PART() or EXTRACT() function.
How to Convert a Specific Timestamp to a UNIX DateTime?
Pass the “EPOCH” as an argument to the DATE_PART() function to convert the given timestamp into a UNIX timestamp. The DATE_PART() will retrieve the converted UNIX timestamp in seconds:
SELECT DATE_PART('EPOCH', NOW()) AS converted_timestamp;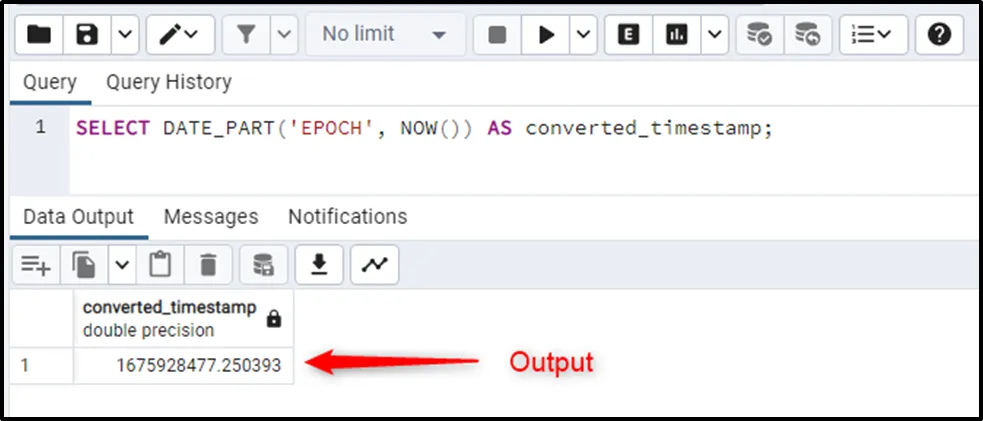
That’s all from this Postgres guide!
Conclusion
In PostgreSQL, different built-in functions are used along with the SELECT statement to query date and time. For instance, to query the current date or time, the CURRENT_DATE, CURRENT_TIME, NOW(), TIMEOFDAY(), CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, and LOCALTIMESTAMP functions are used, to find the interval between two dates/timestamps the AGE() function is used, to extract any part from a timestamp, such as a day, month, year, hour, minute, etc., the DATE_PART() function is used, and so on. This post explained how to query date and time in Postgres using suitable examples.


