PostgreSQL supports various commands and queries to manipulate the tables' data. For example, the CREATE TABLE command creates a new table, the UPDATE TABLE command modifies an existing table, and the DROP TABLE removes a table, etc.
SELECT is one of the most often-used commands in Postgres that selects a specific record, multiple records, or all records from a specific table. The SELECT command is executed with the “*” symbol to select all data from a Postgres table.
This post demonstrates how to select all from a specific Postgres table.
How to Select/Fetch All From a Postgres Table?
Use the “SELECT *” command followed by the FROM clause and then the table’s name to select all from a specific Postgres table:
SELECT * FROM tab_name;
Let’s understand it via the following example.
Example 1: Selecting All From a Table
We have already created a Postgres table named “emp_data”. To fetch all from the “emp_data” table, use the “SELECT *” command:
SELECT * FROM emp_data;
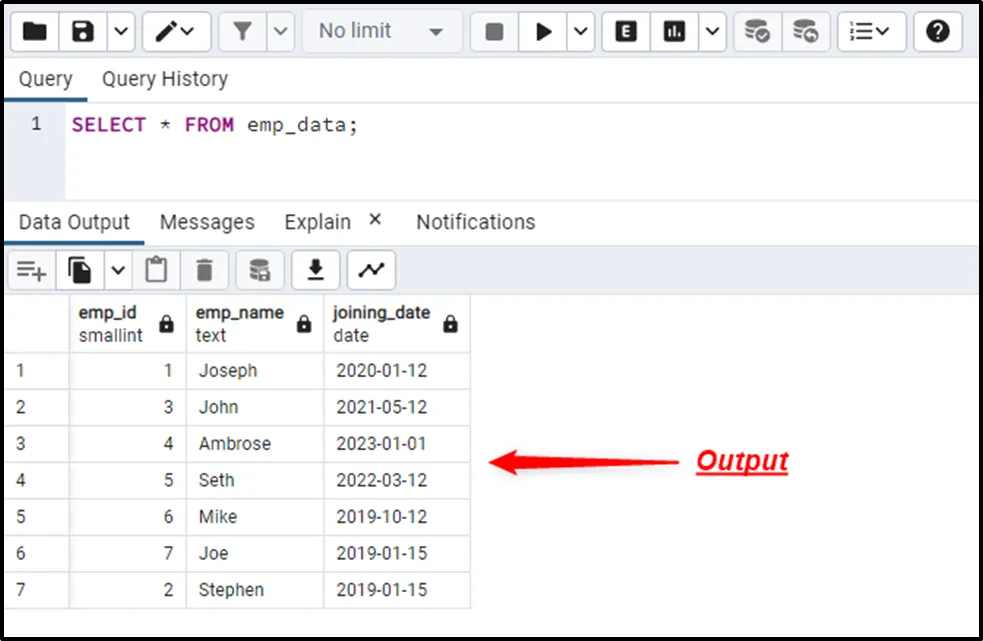
The SELECT * command retrieves all the records from the “emp_data” table.
Example 2: SELECT * With ORDER BY Clause
The ORDER BY clause is optional for sorting a table in ascending or descending order.
SELECT * FROM tab_name [ORDER BY col_name ASC | DESC];
The below code demonstrates how to get all table data in a particular order:
SELECT * FROM emp_data ORDER BY emp_id ASC;
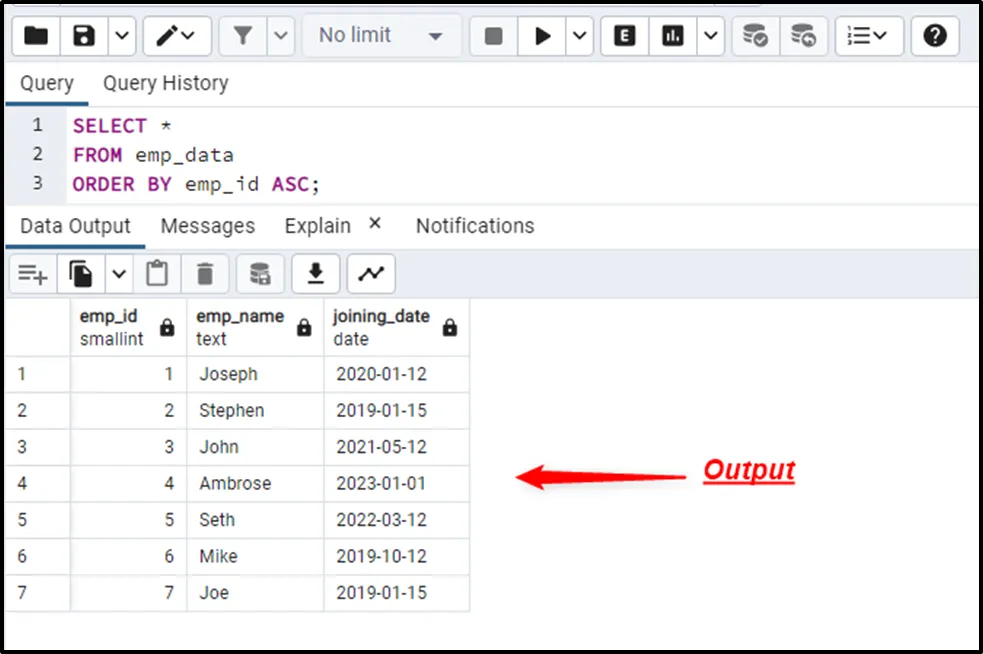
This time, the SELECT * command returns the table’s records in ascending order. To get the data in descending order, use the “DESC” keyword in the ORDER BY clause:
SELECT * FROM emp_data ORDER BY emp_id DESC;
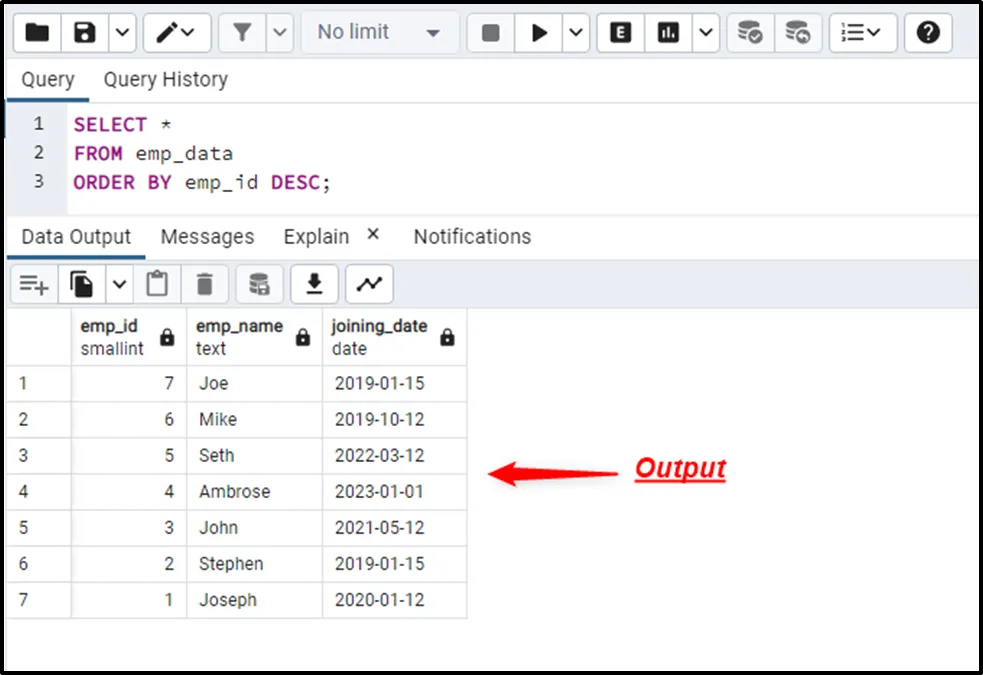
The SELECT * command fetches the table’s data in descending order.
Example 3: SELECT * With GROUP BY Clause
Use the GROUP BY clause with the “SELECT *” command to fetch all the records and divide them into a specific group:
SELECT joining_date, COUNT(emp_id) FROM emp_data GROUP BY joining_date;
In the above snippet, the COUNT() function counts the number of employee ids, and the GROUP BY clause groups the employee’s ids based on their joining_date:
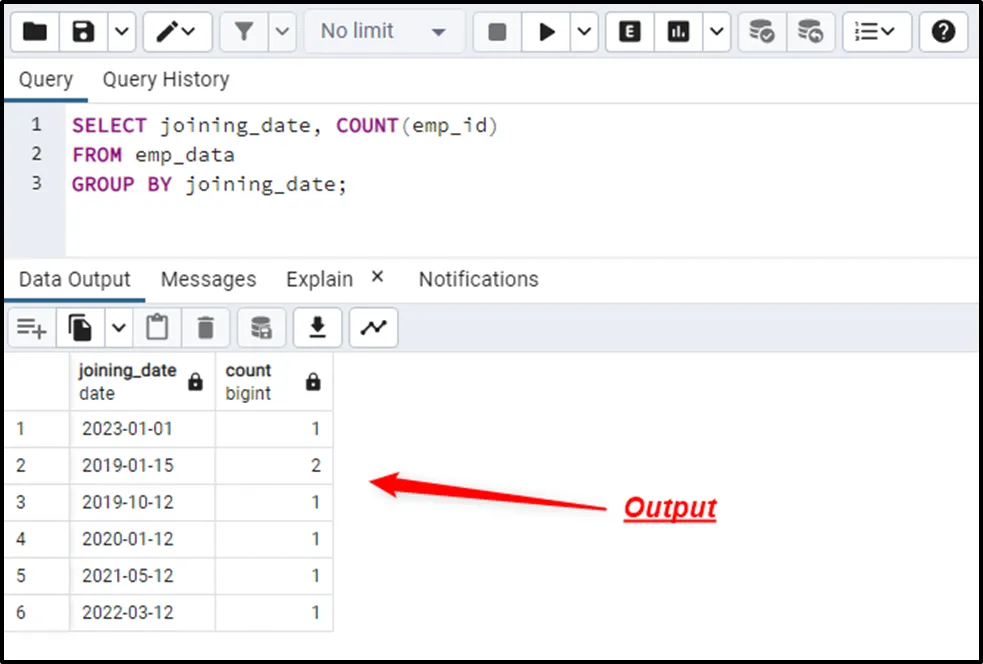
This way, the group by clause groups the table’s data into specific groups.
Conclusion
In PostgreSQL, the SELECT command selects a specific record, multiple records, or all records of a specific table. The SELECT statement is executed with the “*” symbol to select all the data from a particular Postgres table. The ORDER BY clause can be used with the SELECT * command to sort the result set in a particular order. This post presented detailed knowledge on selecting all from a Postgres table.


