CREATE TABLE is a PostgreSQL command for creating tables. In Postgres, attempting to create a table that already exists will result in an error stating that the "relation already exists". To avoid such errors, the IF NOT EXISTS clause can be used with the CREATE TABLE command.
Quick Outline
This write-up will show you how to use the IF NOT EXISTS clause with the CREATE TABLE command.
- How to Create a Table in Postgres?
- Understanding PostgreSQL “CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS” Statement
- CREATE TABLE Vs. CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS - What’s the Difference?
- Conclusion
So, let’s start with table creation.
How to Create a Table in Postgres
In Postgres, the CREATE TABLE command assists us in creating a new table. Here is the very simple yet effective syntax to create a table in PostgreSQL:
CREATE TABLE tab_name( first_col data_type, second_col data_type, third_col data_type, ..... nth_col data_type, );
Here, tab_name represents a table to be created. first_col, second_col, …, nth_col are the column names to be defined in the desired table with their respective data types.
Example #1: Create a Table
Let’s create a new table named “emp_record”:
CREATE TABLE emp_record( emp_id INT PRIMARY KEY, emp_name TEXT, emp_leaves INT, emp_salary INT);
In this example, we created four columns: emp_id, emp_name, emp_leaves, and emp_salaray. The emp_name column has a TEXT data type, while the remaining three columns have an INT data type:
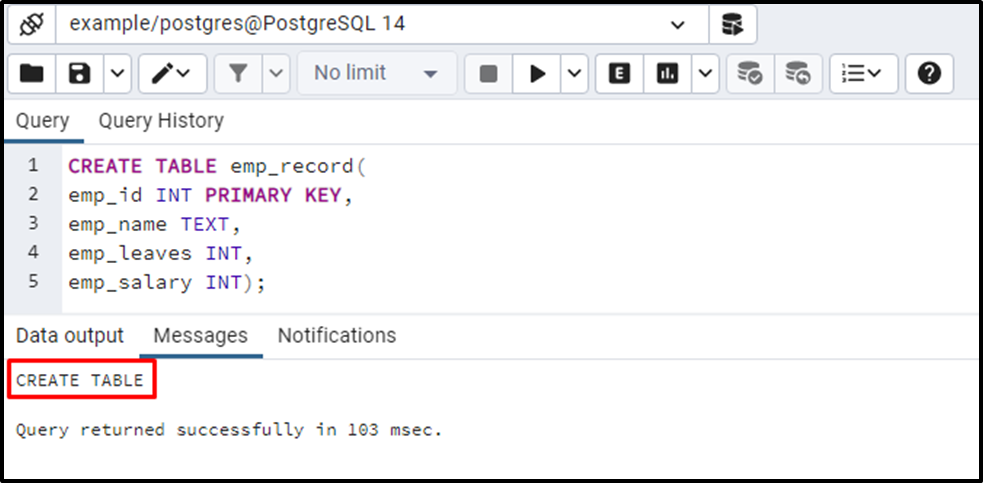
The emp_record table with four columns has been created successfully. Now, you can insert as many records as you want. Let’s insert the following three records into the newly created table:
INSERT INTO emp_record( emp_id, emp_name, emp_leaves, emp_salary) VALUES (1, 'Joe', 1, 40000), (2, 'Seth', 0, 50000), (3, 'John', 2, 45000);
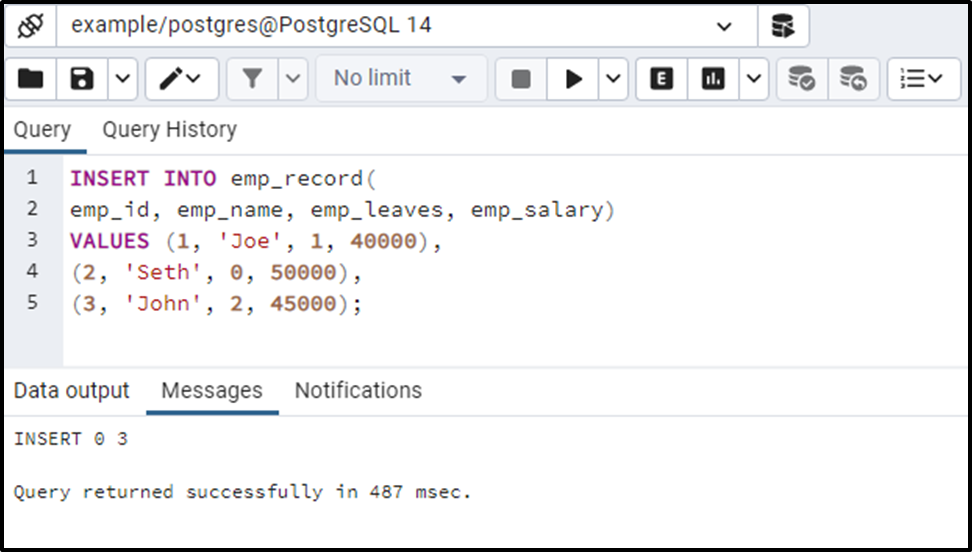
Three new records have been inserted into the emp_record table.
Understanding PostgreSQL “CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS” Statement
If a database already has a table with the same name, then a "relation already exists" error will appear in Postgres. To avoid such a situation, PostgreSQL provides an IF NOT EXISTS clause that can be used with the CREATE TABLE command as follows:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS tab_name( first_col data_type, second_col data_type, third_col data_type, ..... nth_col data_type );
Here, the IF NOT EXISTS clause will first check the existence of the targeted table. If the table already exists, then a notice will be issued instead of throwing an error. However, a new table with the specified name will be created in the database if the desired table doesn’t exist.
Example #1: What is the Need For IF NOT EXISTS Clause?
Let’s create a new table with the same name, i.e., emp_record:
CREATE TABLE emp_record( emp_name TEXT, emp_age INT);
Postgres throws an error stating that the targeted table already exists in the database.
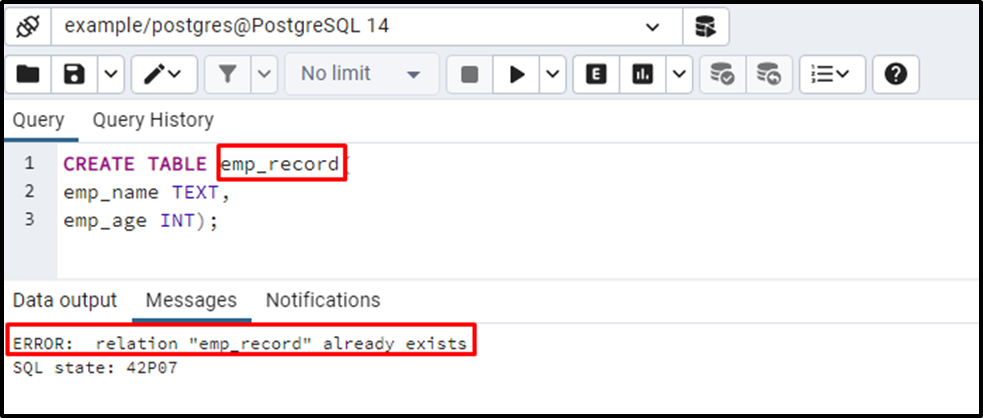
From the above example, it is clear that Postgres throws an error while creating an existing table. The following code will demonstrate how to avoid the “relation already exists” error:
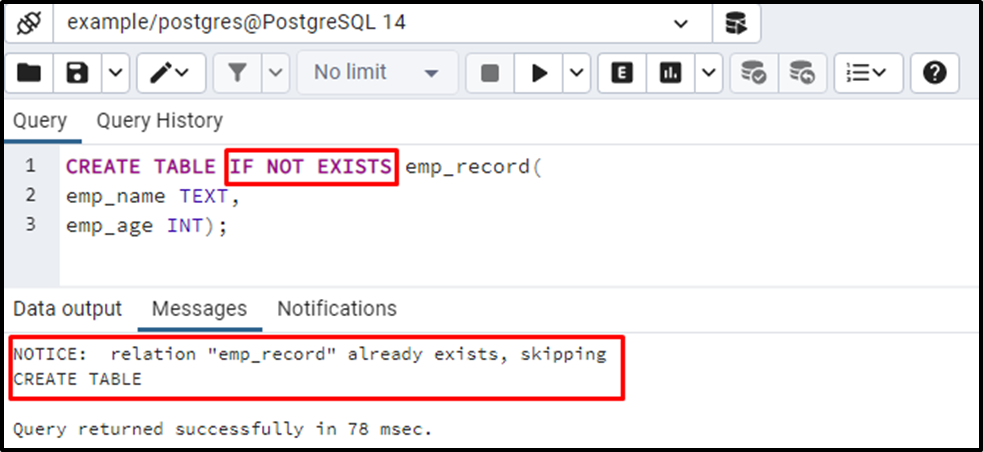
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS emp_record( emp_name TEXT, emp_age INT);
The output clarifies that the IF NOT EXISTS clause shows a notice instead of throwing an error.
CREATE TABLE Vs. CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS - What’s the Difference?
In the case of a simple “CREATE TABLE” statement, the program will be terminated immediately if a table already exists and no further statement will be executed. While in the case of “CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS” a notice will be raised for the create statement and the program’s execution will be moved to the next statement (instead of terminating the program). Let’s learn it via the following example:
DO $$ BEGIN CREATE TABLE test_info( test_id INT PRIMARY KEY, std_name TEXT, score INT); RAISE NOTICE 'Welcome to commandprompt.com'; END $$;
In the above code, the “DO” keyword is used to execute a block, while the BEGIN and END keywords are used to start and terminate the transaction block. Two statements are enclosed in the block, the first one is to create a new table while the other one is to raise a greeting message. Let’s execute it and see the respective output:
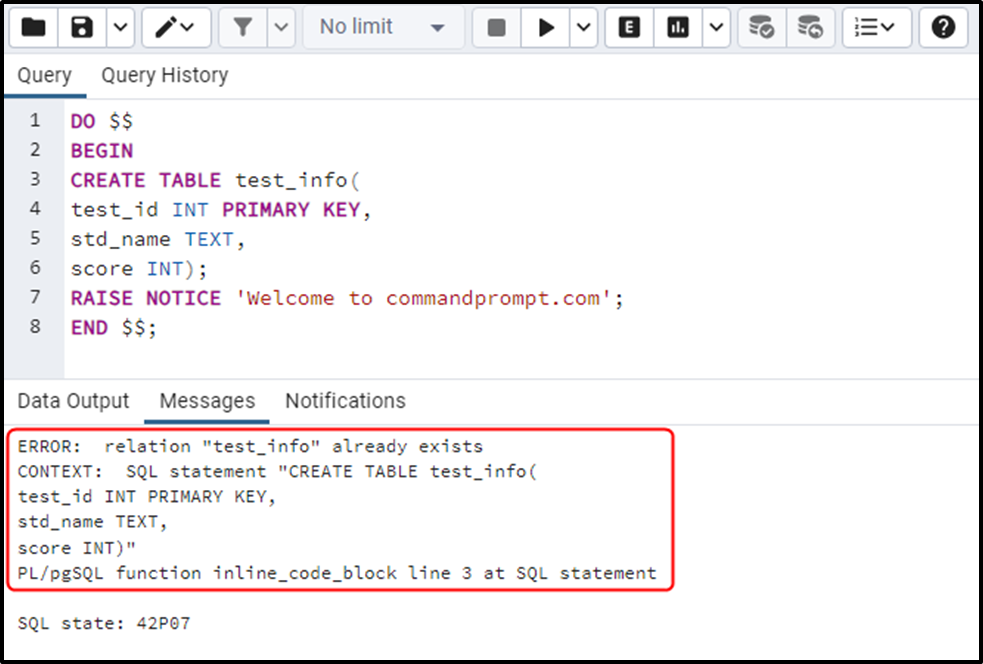
From the output, you can observe that a “relation already exists” error arises and the program terminates immediately. Also, it didn’t execute the remaining statements.
Let’s use the same code with the “IF NOT EXISTS” option and see how it works:
DO $$ BEGIN CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS test_info( test_id INT PRIMARY KEY, std_name TEXT, score INT); RAISE NOTICE 'Welcome to commandprompt.com'; END $$;
This time a notice is raised indicating that the relation to be created already exists in the database. Postgres skips the “CREATE TABLE” statement and moves the control to the subsequent statement, which gets executed successfully:
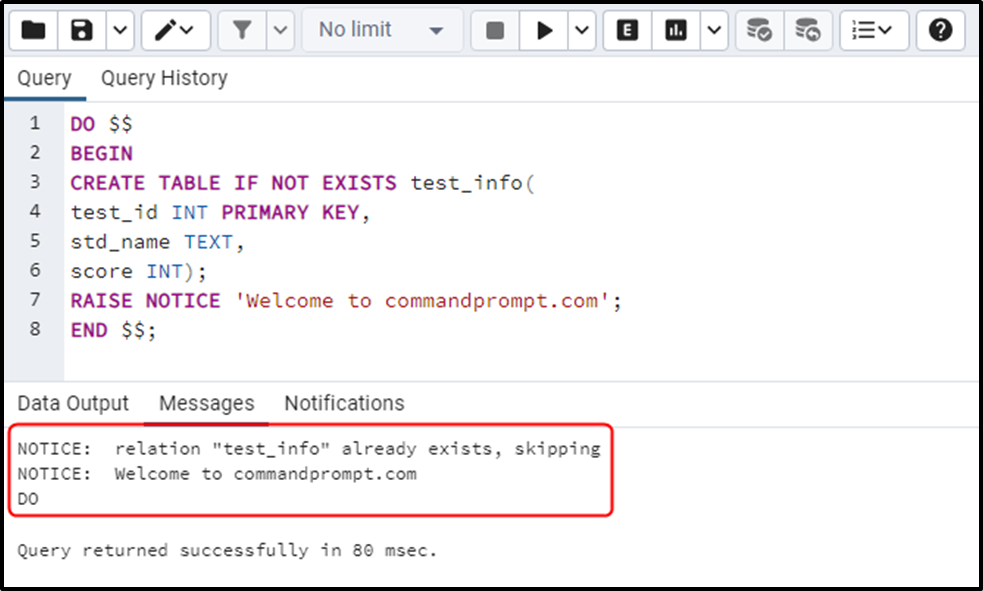
In this way, you can use the IF NOT EXISTS clause with the CREATE TABLE command to avoid the “relation already exists” error.
Conclusion
In PostgreSQL, the CREATE TABLE command assists us in creating a new table. In Postgres, attempting to create a table that already exists will result in an error stating that the "relation already exists". To avoid such errors, the IF NOT EXISTS clause is used with the CREATE TABLE command. This article used various examples to demonstrate how the PostgreSQL CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS command works in PostgreSQL.



