PostgreSQL provides various window functions that help us in performing calculations across the rows related to the current row. These functions serve various benefits/functionalities such as computing cumulative sums, assigning ranks to the rows within the partitions, and so on.
This write demonstrates how to use FIRST_VALUE Function in Postgres using the following outlines:
- Applying FIRST_VALUE() Function Over a Particular Table
- Applying FIRST_VALUE() Function Over Table Partitions
How to Use the FIRST_VALUE() Function in PostgreSQL?
PostgreSQL offers several built-in window functions with different functionalities. FIRST_VALUE() is one of them that retrieves the first value in the sorted partition/window of a result set.
FIRST_VALUE (exp) OVER ( [PARTITION BY partition_col_list] [ORDER BY order_col_list] );
Here,
- “exp” represents an expression that can be any valid column, expression, or subquery. It must retrieve a single value.
- “[PARTITION BY partition_col_list]” is an optional clause that splits the result set into partitions based on columns specified in “partition_col_list”. However, if you don't use it, the stated function will consider the entire result set as one partition.
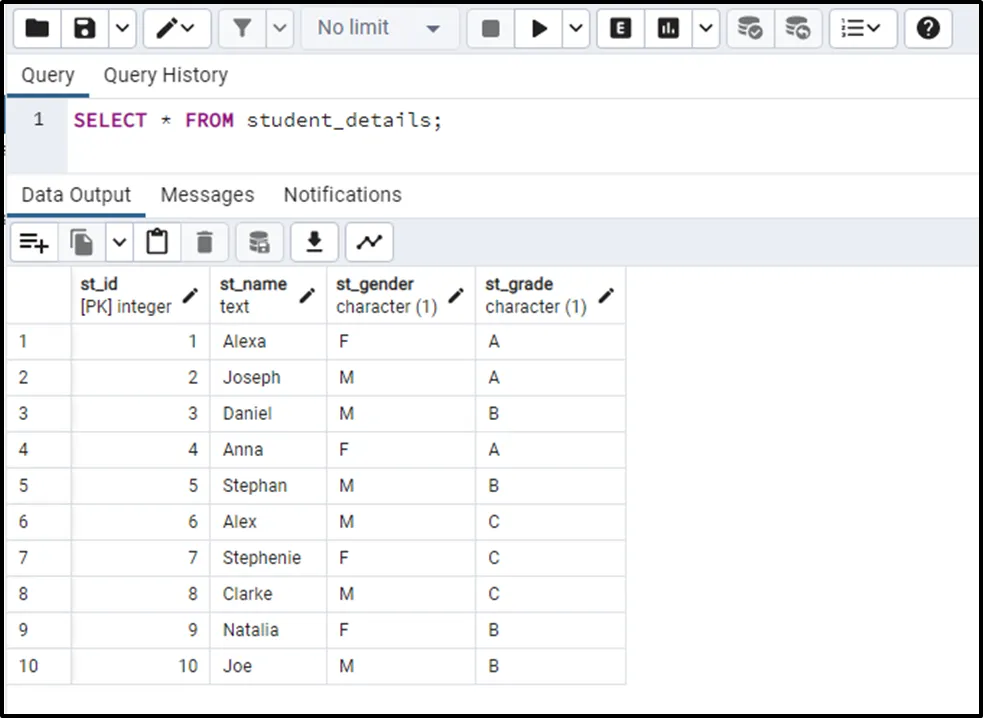
Sample Table
Let’s fetch the data of a sample table named “student_details” using the following statement:
SELECT * FROM student_details;
Example 1: Applying FIRST_VALUE() Function Over Entire Table
In this example, we will apply the FIRST_VALUE() function on the “student_details” table:
SELECT st_id, st_name, st_gender, st_grade, FIRST_VALUE(st_name) OVER( ORDER BY st_grade ) FROM student_details;
In the above code snippet:
- The PARTITION BY Clause is skipped, so the FIRST_VALUE() function will consider the entire table as one partition.
- Each partition will be sorted in default (ascending) order based on the “st_grade” column.
- The FIRST_VALUE() function will pick the first value from the “st_name” column:
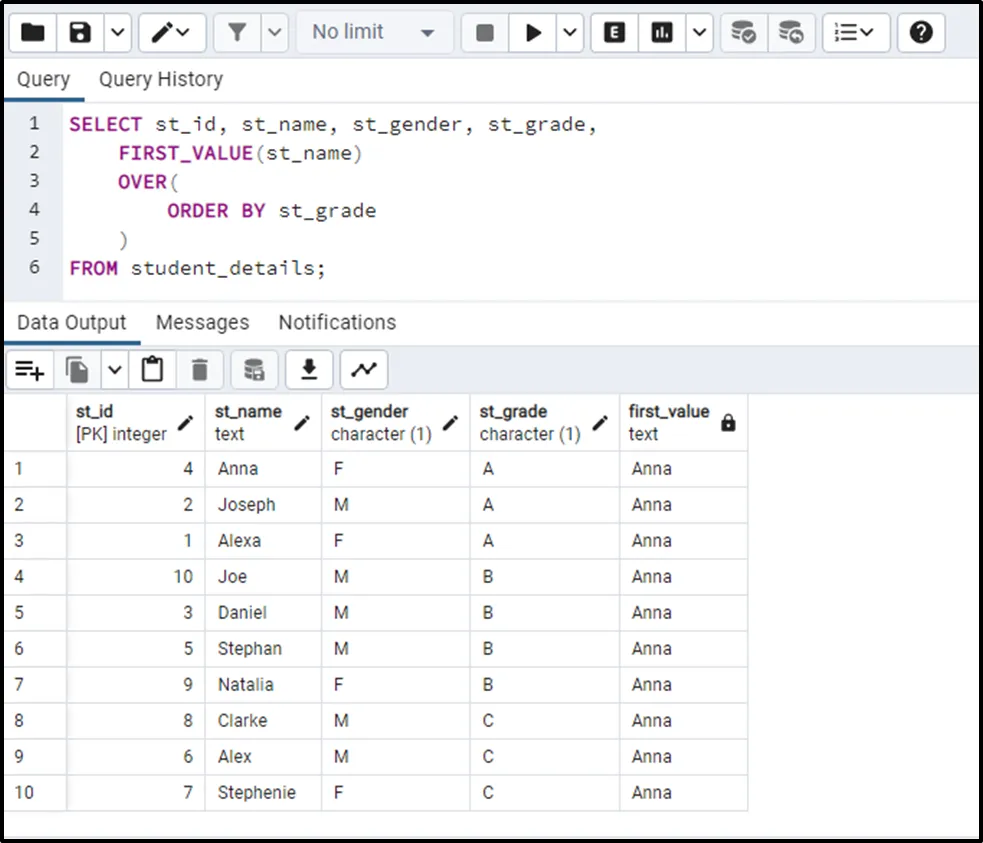
The output demonstrates that FIRST_VALUE() selects a value from the first row of the sorted table.
Example 2: Applying FIRST_VALUE() Function Over Table Partitions
In this example, we will apply the FIRST_VALUE() function on the table’s partition instead of the entire result set:
SELECT st_id, st_name, st_gender, st_grade, FIRST_VALUE(st_name) OVER( PARTITION BY st_gender ORDER BY st_grade ) ; FROM student_details;
In the above code snippet:
- Partitions are created based on the “st_gender” column.
- Each partition will be sorted based on the “st_grade” column.
- The FIRST_VALUE() function will pick the first value from the “st_name” column while staying within its associated partition:
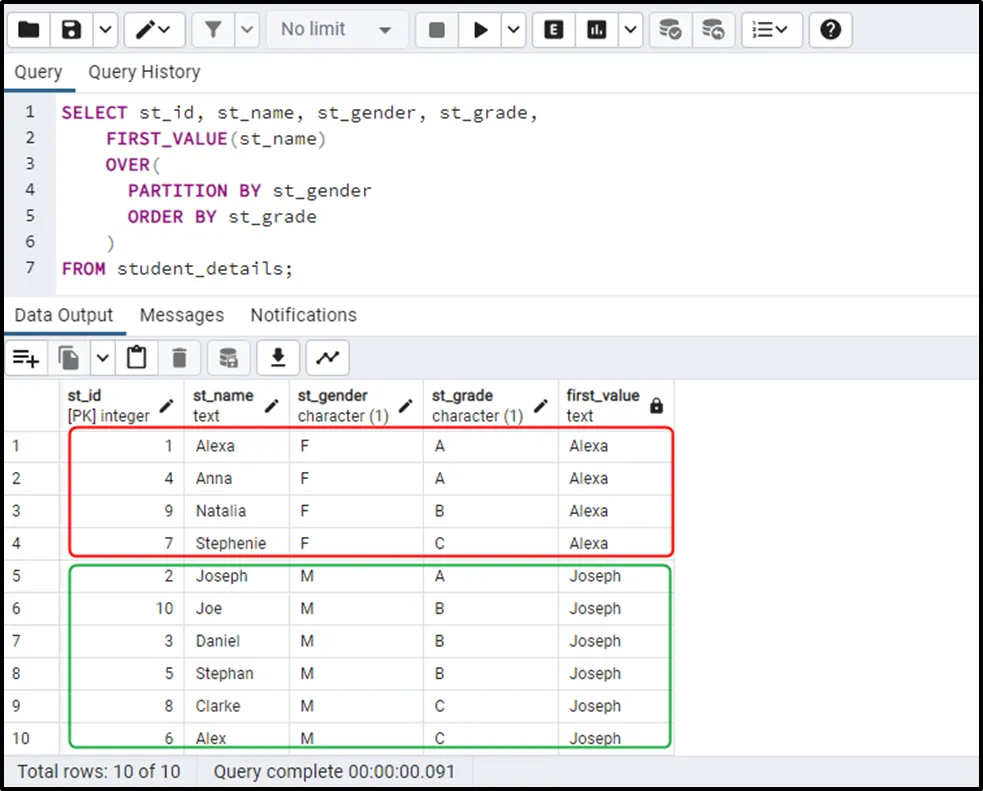
The output demonstrates that the FIRST_VALUE() function selects a value from the first row based on its partitions.
Conclusion
FIRST_VALUE() is one of the Window functions in Postgres that retrieves the first value in the sorted partition/window of a result set. The FIRST_VALUE() function picks the first value from the selected column while staying within its associated partition. If the PARTITION BY Clause is skipped/ignored, the FIRST_VALUE() function will consider the entire table as one partition. This write-up has demonstrated various use cases of the FIRST_VALUE() function.


